Apprenticeship programs have been around for centuries. In the most basic sense, an apprentice is somebody learning the skills of a particular trade by working with a skilled worker. In industrialized countries, apprenticeship programs vary greatly from regulated arrangement between private companies and schools and/or trade unions to less formal arrangements in which a person new to a field of endeavor works along-side somebody already skilled in that field. Most apprenticeship programs include classroom work as well as on-the-job training.
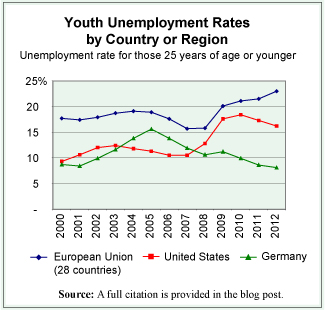
There are many things that play a role in the fluctuations of unemployment rates and these rates tend to be higher for younger people than for those more established in their work lives. Thus, having a youth population that is well trained for the jobs that are available seems a natural aid to keeping the youth unemployment rate down. From the data available on countries of the European Union—where the prevalence of apprenticeship programs is greater than in the United States, although it does vary from country to country—there seems to be a discernible connection between lower youth unemployment rates and the prevalence of robust apprenticeship programs. By way of comparison, we offer the graph that shows the youth unemployment rate for the first decade of the current century for the European Union, for Germany, and for the United States.
While the youth unemployment rate in the European Union as a whole, in 2012, was 23% it ranged widely from a low of 8.1% in Germany to a high of 55.3% in Greece. Interestingly, the two European countries with the lowest youth unemployment rate are also two of the countries in the Union with the most robust apprenticeship programs, Germany and Austria.
In the United States, apprenticeship programs are not as heavily used as they are in Europe. Trade unions use to be a primarily source of such programs in the United States but with the decline in union membership over the last decades these programs have also been in decline. That is until recently. European companies are starting to establish apprenticeship programs in the United States to train the workforce they need for their U.S. facilities.
Today’s market size is the number of people in the United States participating in apprenticeship programs that are registered with the U.S. Department of Labor. The approximate number participating in such programs in Germany is also provided.
Geographic reference: United States and Germany
Year: 2012
Market size: United States: 358,000 (with an additional, approximately 450,000 involved in programs not registered with the Department of Labor)
Market size: Germany: 1.6 million
Sources: (1) “Registered Apprenticeship National Results,” U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration, June 7, 2013, available online here. (2) Unemployment Rate by Age Group,” Eurostat, October 31, 2013, available online here. (3) “Apprenticeships: Earn while you learn,” Bureau of Labor Statistics, Summer 2013, available online here.
Original Source: U.S. Department of Labor and Eurostat
Posted on December 2, 2013